
Phalaenopsis Orchid Health and Anatomy Just Add Ice Orchids
However, botanists generally agree that one feature above all others defines the orchid and differentiates it from virtually all other flowering plants: the fusion of the male portion of the flower (stamen) and female portion (pistil) into one structure called the column—often visible protruding from the center.
Orange Slices The Anatomy of an Orchid
The structure of an orchid plant is the same as any plant for it has roots, stems, leaves and flowers. But these parts are adapted to its way of life and differ somewhat from familiar plants which you grow in your garden. Epiphytes and Terrestrials

Structure And Function What Makes an Orchid an Orchid Smithsonian Gardens
Plant anatomy, or phytotomy, is divided into four major structures: 1) roots 2) stems 3) leaves 4) all the parts of the reproductive cycle of the orchid. Below is a list of basic orchid terminology and some pictures to represent each. I've tried to keep this more readable and not as boring as reading a dictionary, or an atlas.

Schematic view of main orchid vegetative and reproductive structures.... Download Scientific
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae ( / ˌɔːrkɪˈdeɪsi.iː, - si.aɪ / ), [2] a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant. Orchids are cosmopolitan plants that are found in almost every habitat on Earth except glaciers.

Phenotypes of orchid. (A) Diagram showing orchid flower organs (adapted... Download Scientific
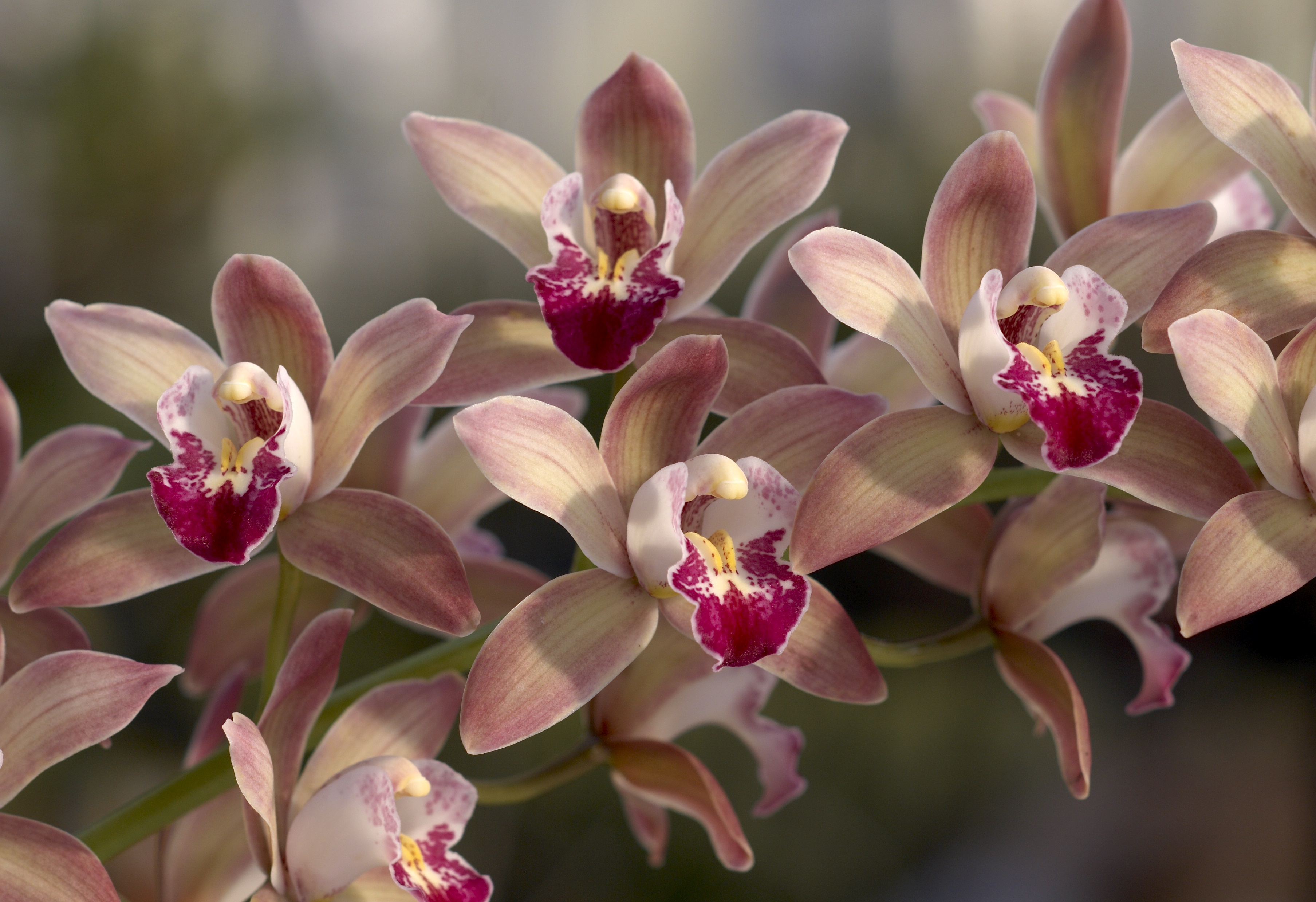
Care and Culture The orchid flower is full of intricate parts. And while there can be variation from genus to genus, all have fairly similar parts. Let's take a closer look at a Phalaenopsis orchid to better understand the flower's structure.
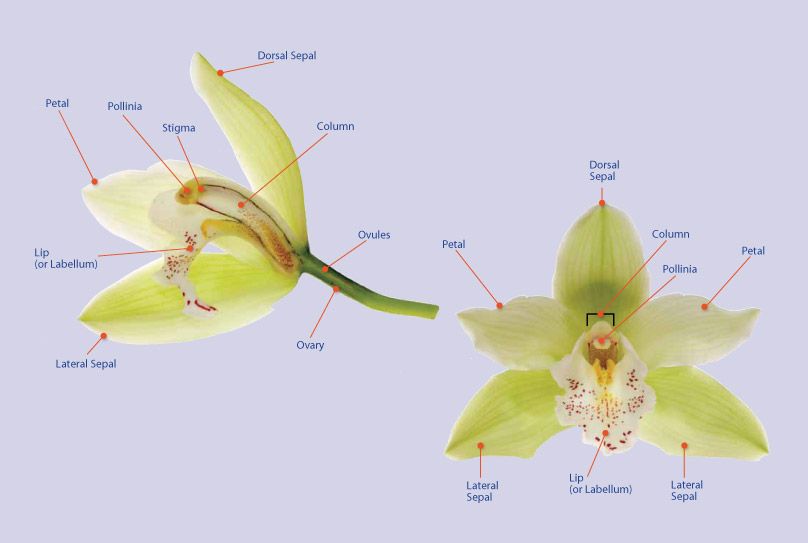
orchid parts Archives Plant Talk
Phragmipedium orchid. ©iStock.com/Wirestock With almost 30,000 species across 880 genera, the Orchidaceae family is the most diverse family of flowering plants on Earth. This family has evolved over a period of almost 120 million years to thrive in a range of climates and habitats.

Die Struktur Der Orchideenblume Vektor Abbildung Illustration von ausbildung, graphik 97937894
In most orchids, the flowers rotate 180° as they develop, so that the labellum is the lowest of the petals, facing upward. Instead of separate stamens and pistils, orchids have a combined reproductive organ-the column-in which two stigmas are merged with a single stamen, and the third stigma is modified into a tiny structure, the rostellum.
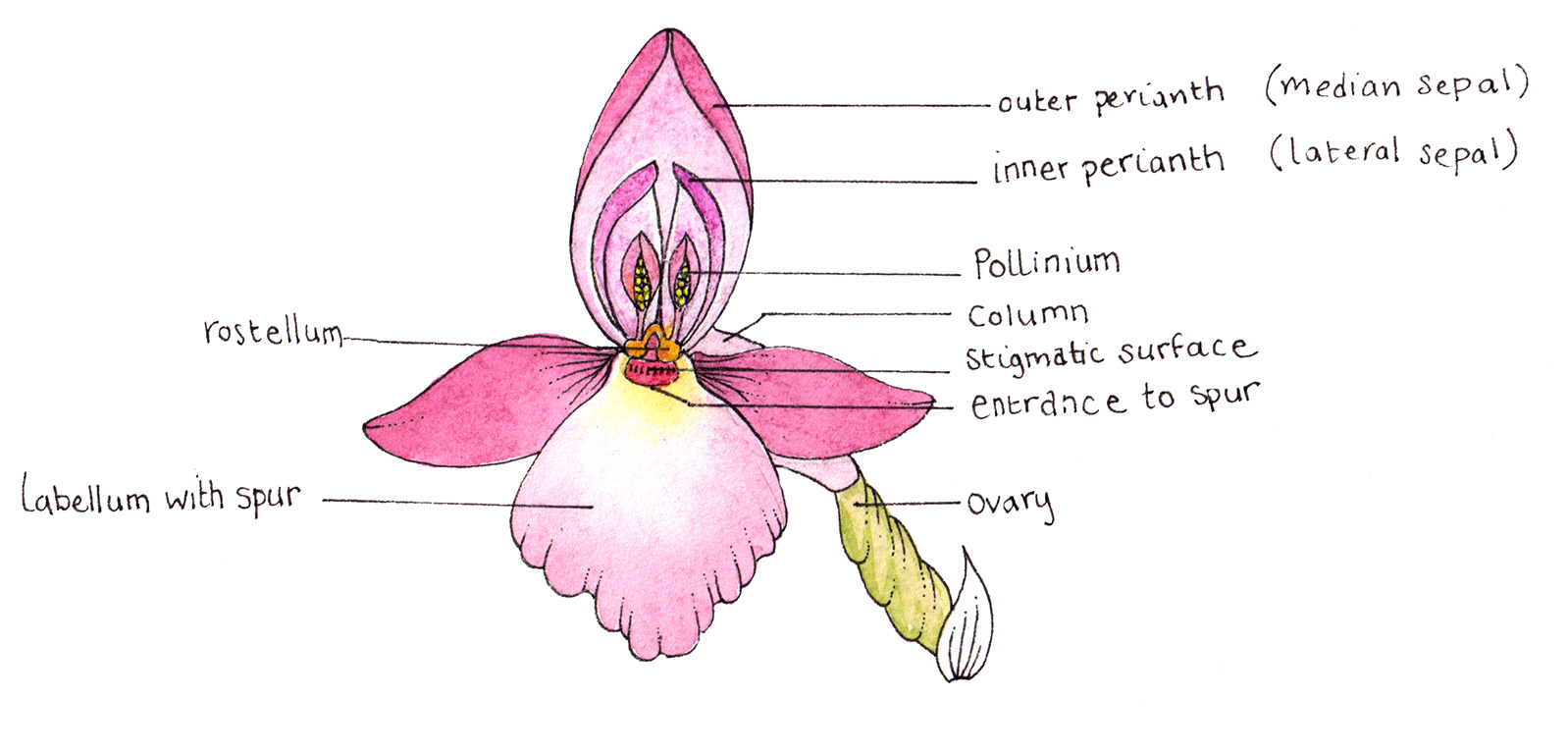
Orchid diagram labelled Lizzie Harper
Structural diversity Learn about orchids and observe an orchid expert pollinating a lady's slipper orchid with the pollen of a second fine specimen, and the method of cross-breeding in a laboratory Learn about orchids, including the lady's slipper. See all videos for this article

Structure of the Orchid by isijeh on DeviantArt
1. appearance. The pseudobulbs and canes are like the humps on camels, storing food and water to sustain the plant during droughty conditions. They perform a vital function to the plant even when leafless. Front bulbs are the pseudobulbs on the younger part or the plant. The front bulbs are the actively growing part of your plant and it is from.

Pin on Orchids (including at National Orchid Garden)
The most distinctive aspect of orchid floral anatomy is the column, the single reproductive structure formed by the fusion of the male stamens and female style, which are separated in the vast majority of plant families. Most orchids have a single fertile anther (flower structure where pollen is produced) located at the tip of the column.
Orange Slices The Anatomy of an Orchid
Orchids have a unique flower structure which consists of four main parts. The orchid flower is typically has an outer whorl of three sepals, an inner loop of three petals, a single large column in the center, and an enlarged bottom petal called a lip or labellum.
Wild Nature of the Cantabrian Mountains (Spain) Structure of an orchid flower
A central structure known as the column is a unique adaptation of orchids that houses both the male (anther) and female (stigma) parts of the flower (Roberts and Dixon 2008). The column—at least the distal (away from the center) portion—is oriented horizontally. The anther is located at the distal end of the column.
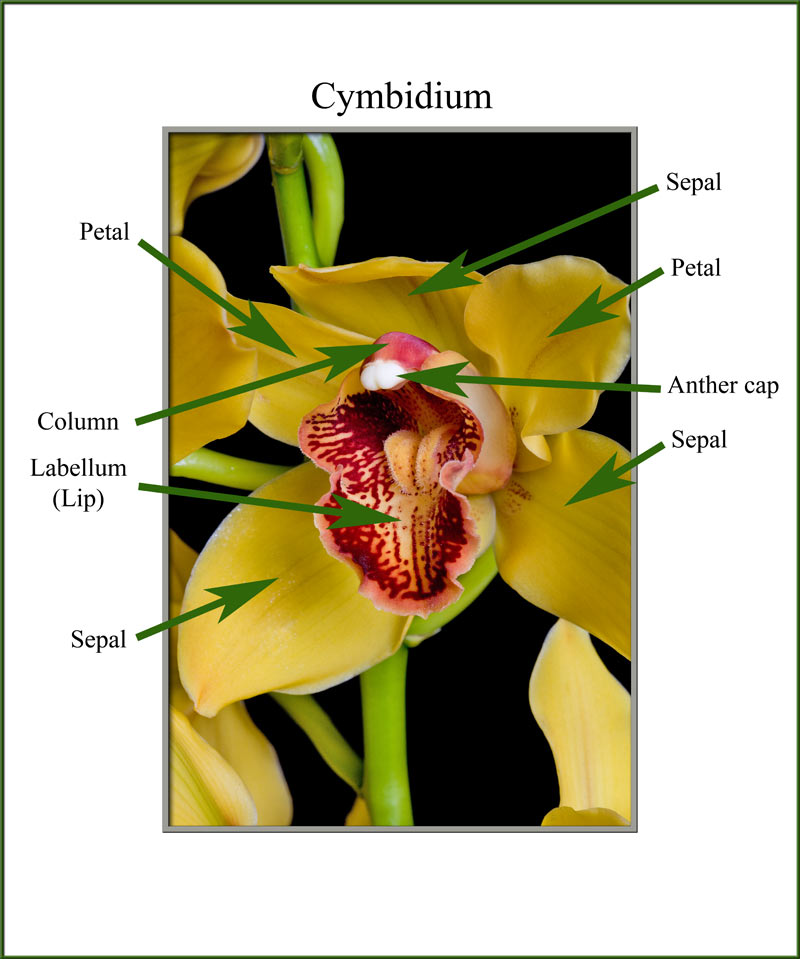
Cymbidium Orchid Anatomy Orchid Flowers
Plant parts are divided into four main structures: Roots Stems Leaves Flowers (which includes the parts for its reproductive cycle) We'll explore the more unfamiliar of these basic terms. You'll find all that information with diagrams below! Enjoy! 1.Roots

The Orchid Flower Structure Biological Science Picture Directory
Home Science Plants Flowering Plants Characteristic morphological features orchid Orchid (Vanda). The primary characteristics that distinguish the orchids as a group are found in the flower. At the bottom of an unspecialized non-orchid flower is the stem that supports it, called the pedicel.
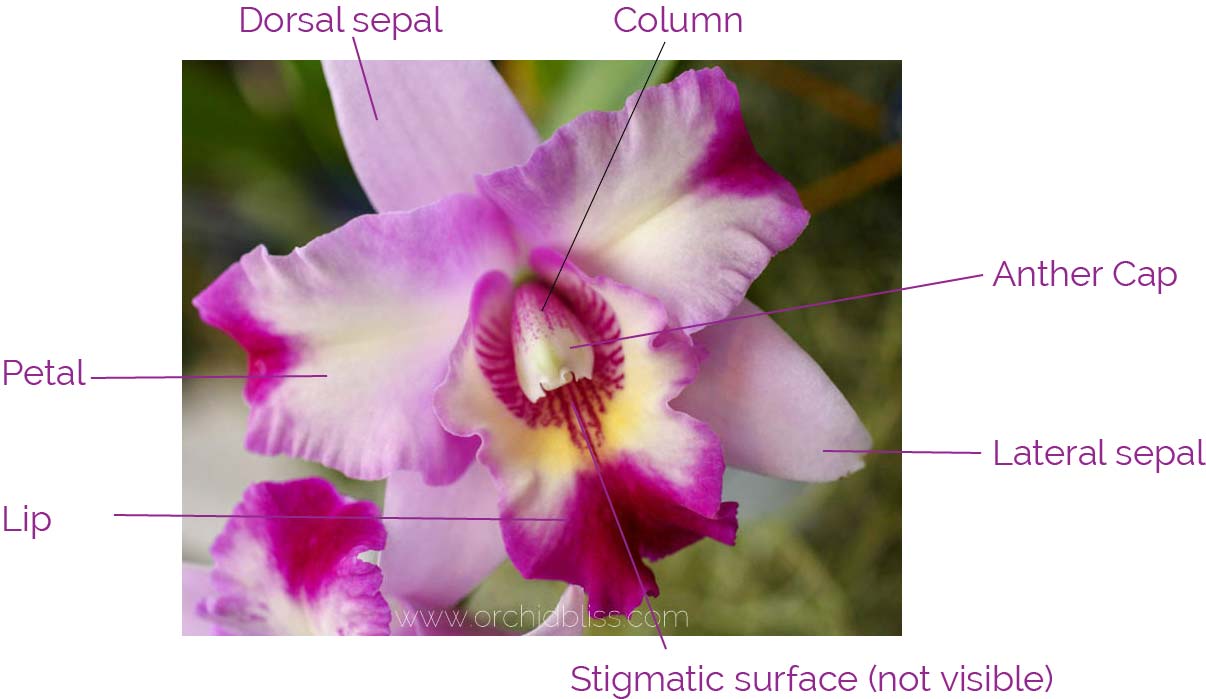
Orchid Anatomy and Terminology A Glossary of Orchid Terms
Floral Organ Identity Genes in Orchids. The structure of the orchid flower has a zygomorphic nature in contrast to most plant groups leading to precise interaction with the pollinator (Cubas, 2004). Orchid flowers generally contain an outer whorl with three sepals, an inner whorl with three petals, and a single column in the center.

Diagram showing orchid flower organs (adapted from Tsai et al. 2005). Orchid flowers have three
orchid species have only one stamen in the flower, which is a characteristic feature of the Orchidaceae (Kew Royal Botanic Gardens 2013). Most orchid flowers have the same basic reproductive structures (Figure 1). A central structure known as the column is a unique adaptation of orchids that houses both